Main page (Russian)
 Search in database (English)
Search in database (English)
Properties of substance:
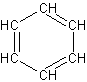
benzene
skc-fileSynonyms:
benzole
Group of substances:
organic
Physical appearance:
colorless liquidEmpirical formula (Hill's system for organic substances):
C6H6Structural formula as text:
C6H6Molar/atomic mass: 78.1118
Melting point (°C):
5.533Boiling point (°C):
80.103CAS №: 71-43-2
Solubility (g/100 g of solvent):
1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane: miscible [Ref.]
acetic acid: miscible [Ref.]
acetone: miscible [Ref.]
ammonia liquid : moderately soluble [Ref.]
chloroform: miscible [Ref.]
diethyl ether: miscible [Ref.]
diethylene glycol: 52 (20°C) [Ref.]
ethanol: miscible [Ref.]
ethylene glycol : 5.83 (20°C) [Ref.]
ethylene glycol : 6 (25°C) [Ref.]
ethylene glycol : 6.61 (40°C) [Ref.]
ethylene glycol : 7.61 (60°C) [Ref.]
formic acid 95%: 15.14 (25°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 1.56 (-20°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 1.67 (-15°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 1.88 (-10°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 2.05 (-5°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 2.3 (0°C) [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : 3.11 (15°C) [Ref.]
oxygen liquid: 0.00098 (-195.6°C) [Ref.]
sulfolane: miscible [Ref.]
water: 0.153 (0°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.1807 (9°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.181 (20°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.185 (30°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.1902 (41°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.207 (51°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.2299 (61°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.4106 (99.99°C) [Ref.]
water: 2.17 (200°C, with pressure 65 bar) [Ref.]
water: 1.78 (200°C, with pressure 400 bar) [Ref.]
water: miscible (270°C) [Ref.]
Numerical data:
Year of discovery: 1825
Teoretic number of isomers: 217
Teoretic number of isomers: 328
Polarizability of molecules (nm3): 0.0104
Magnetic susceptibility (mm3/mol): -0.0648
Density:
0.90006 (0°C, g/cm3)
0.8895 (10°C, g/cm3)
0.879 (20°C, g/cm3)
0.8685 (30°C, g/cm3)
0.8576 (40°C, g/cm3)
0.8357 (60°C, g/cm3)
0.8145 (80°C, g/cm3)
Synthesis 1:
Reference: Гитис С.С., Глаз А.И., Иванов А.В. Практикум по органической химии: Органический синтез. - М.: Высшая школа, 1991 pp. 186-187 18,6 gr of aniline is dissolved in a mixture of 60 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 100 ml of water in porcelain beaker, equiped with a stirrer, a dropping funnel and a thermometer. The mixture is cooled on an ice bath until 0 C (small pieces of ice are placed into the beaker if necessary). 14,4 gr of sodium nitrite in 60 ml of water is added slowly from the dropping funnel to the cooled mixture of aniline hydrochloride. After addition of all sodium nitrite the mixture should give the reaction on potassium iodide starch test paper and have the acidic reaction on indicator paper. the solution, which was obtained by mixing 54 gr of SnCl2*2H2O in 60 ml of water and 70 gr of sodium hydroxide in 140 ml of water, is added to the diazosolution with caution and cooling. The rate of addition of this mixture depends on the intensity of releasing of nitrogen. Then the contents of the beaker is placed into a round-bottom flask and formed benzene is distilled with water steam. Water is separated in a separation funnel, benzene is dried with fused calcium chloride and distilled from a Wurtz flask.
The yield is 4,2 gr (27% from theory).
Benzene is a colourless liquid with boiling point at 80 C, d(20/4)=0,8790, n(20 C, D-line)=1,50165
UV-spectrum [λmax (lg e) ]: 184 nm (4,78) (in n-heptane). Spectrum NMR (in CCl4): singlet 7,24 ppm
Synthesis 2:
Reference: Реформатский С.Н. Начальный курс органической химии. - М.-Л.: ГИ, 1930 pp. 97
Well-mixed 25 gr of benzoic acid and 50 gr of caustic lime is heated in a copper or glass high-fusing retort, connected with a condenser and a receiver. Benzene, which is obtained in the receiver, is dried with calcium chloride and distilled with a thermometer. The boiling point is 80,4 C.
The yield is 12-14 gr.
Reactions of synthesis:
- Yeild 80%. [Ref.1]
3C2H2 → C6H6
- Yeild 93%. [Ref.1
 ]
]
C6H5Br + 2NH4Cl + Zn → C6H6 + ZnCl2 + NH4Br + NH3
Reactions:
- Yeild 80-95%. [Ref.1]
C6H6 + NO2BF4 → C6H5NO2 + HBF4
- Yeild 80%. [Ref.1
 ]
]
C6H6 + (CH3)2CHOH → (CH3)2CHC6H5 + H2O
- Yeild 70-80%. [Ref.1, Ref.2
 , Ref.3]
, Ref.3]
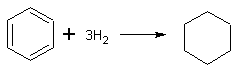
- Yeild 48-53%. [Ref.1
 , Ref.2
, Ref.2 , Ref.3
, Ref.3 ]
]
C6H6 + Br2 → C6H5Br + HBr
- Yeild 32%. [Ref.1
 ]
]
C6H6 + CH2=CHCH2Cl → C6H5CH2CHClCH3
- Yeild 50%. [Ref.1]
C6H6 + C2H5Cl → C6H5C2H5 + HCl
- Yeild 45%. [Ref.1
 ]
]
2C6H6 + 3H5IO6 + 9HI → 2C6I6 + 18H2O
- [Ref.1]
C6H5CH=CH2 + C6H6 → (C6H5)2CHCH3
- [Ref.1, Ref.2]
C6H6 + CH3CH=CH2 → C6H5CH(CH3)2
Refractive index (nD):
1.50112 (20°C)
1.49478 (30°C)
Vapour pressure (Torr):
1 (-45°C)
10 (-11.6°C)
40 (7.5°C)
100 (26.1°C)
400 (60.6°C)
Dissociation:
pKBH+ (1) = -9.2 (0°C, hydrogen fluoride )
pKa (1) = 37 (20°C, water)
Retention indices for gas chromatography:
656,1 (phase - DB-5, temperature-programmed conditions, 6 K/min)
Permittivity (dielectric constant):
2.284 (25°C)
Surface tension (mN/m):
28.22 (25°C)
25 (50°C)
21.77 (75°C)
Speed sound (m/s):
202 (97.1°C, aggregative state - gas)
Standard molar enthalpy (heat) of formation ΔfH0 (298.15 K, kJ/mol):
-82.98 (l)Standard molar entropy S0 (298.15 K, J/(mol·K)):
269.38 (l)Molar heat capacity at constant pressure Cp (298.15 K, J/(mol·K)):
81.6 (l)Molar enthalpy (heat) of fusion ΔfusH (kJ/mol):
9.843Enthalpy (heat) of vaporization ΔvapH (kJ/mol):
30.76Flash point (°C):
-11Autoignition temperature (°C):
534Heat of combustion (kJ/mol):
3273.1Gas phase basicity ΔbaseG (298 K, kJ/mol)
-725.4 (g) [Ref.]
Enthalpy (heat) of solution ΔsolH (J/mol)
619 (l) [solvent: methanol, 25 C, 1 mol substance : 1 mol solvent] [Ref.]
LD50 (mg/kg):
6400 (rats, oral)
8100 (rats, oral)
1800 (rats, oral)
4700 (mice, oral)
5700 (mice, oral)
5000 (mice, oral)
340 (mice, intraperitoneal)
Critical temperature (°C):
289.41Critical pressure (MPa):
4.92Critical density (g/cm3):
0.307References:
- Lewis R.J. Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. - 11ed. - Wiley-interscience, 2004. - pp. 360-361
- Seidell A. Solubilities of organic compounds. - 3ed., vol.2. - New York: D. Van Nostrand Company, 1941. - pp. 368-370
- Smallwood I.M. Handbook of organic solvent properties. - 1996. - pp. 35-37
- Yalkowsky S.H., Yan H. Handbook of aqueous solubility data. - CRC Press, 2003. - pp. 238-242
- Воскресенский П.И., Каверина А.А., Парменов К.Я., Цветков Л.А., Эпштейн Д.А. Справочник по химии. - 4 изд. - М.: Просвещение, 1978. - pp. 200 [Russian]
- Вредные вещества в промышленности: Справочник для химиков, инженеров и врачей. - 7-е изд., Т.1. - Л.: Химия, 1976. - pp. 88-97 [Russian]
- Вредные химические вещества: Углеводороды, галогенпроизводные углеводородов. Справочник. - Л.: Химия, 1990. - pp. 115-140 [Russian]
- Гордон А., Форд Р. Спутник химика. - М.: Мир, 1976. - pp. 186, 462 [Russian]
- Гурвич Я.А. Справочник молодого аппаратчика-химика. - М.: Химия, 1991. - pp. 229 [Russian]
- Некрасов Б.В. Основы общей химии. - Т.1. - М.: Химия, 1973. - pp. 550-551 [Russian]
- Новый справочник химика и технолога. Общие сведения. Строение вещества. Физические свойства важнейших веществ. Ароматические соединения. Химия фотографических процессов. Номенклатура органических соединений. Техника лабораторных работ. Основы технологии. Интеллектуальная собственность. - СПб.: НПО Профессионал, 2006. - pp. 557-605 [Russian]
- Огородников С.К., Лестева Т.М., Коган В.Б. Азеотропные смеси: Справочник. - Л.: Химия, 1971. - pp. 282 [Russian]
- Промышленные хлорорганические продукты: Справочник. - М.: Химия, 1978. - pp. 620-622 [Russian]
- Рабинович В.А., Хавин З.Я. Краткий химический справочник. - Л.: Химия, 1977. - pp. 129 [Russian]
- Справочник по растворимости. - Т.1, Кн.1. - М.-Л.: ИАН СССР, 1961. - pp. 432-433 [Russian]
- Справочник по растворимости. - Т.1, Кн.2. - М.-Л.: ИАН СССР, 1962. - pp. 1111, 1263 [Russian]
- Справочник химика. - 2 изд., Т.1. - Л.-М.: Химия, 1966. - pp. 553 [Russian]
- Справочник химика. - Т. 3. - М.-Л.: Химия, 1965. - pp. 634 [Russian]
- Химическая энциклопедия. - Т. 1. - М.: Советская энциклопедия, 1988. - pp. 268-269 [Russian]
- Химия и жизнь. - 1990. - №5. - pp. 82 [Russian]
- Энциклопедия для детей. - Т.17: Химия. - М.: Аванта+, 2004. - pp. 376, 380-381 [Russian]
Your requests if no data into database
© Collected Ruslan Anatolievich Kiper, burewestnik@mail.ru